HYCO Plant
One of the most important obstacles in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries is the presence of unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds as well as toxic and harmful compounds, both for compliance with the process and for the environment issues.
One of the most important obstacles in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries is the presence of unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds as well as toxic and harmful compounds, both for compliance with the process and for the environment issues.
One of the most important obstacles in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries is the presence of unsaturated hydrocarbon compounds as well as toxic and harmful compounds, both for compliance with the process and for the environment issues. For example, in the oil industry, the presence of benzene compounds in the gasoline cut, despite having a high-octane number, is one of the factors affecting human health and the environment, or the presence of unsaturated compounds in the lubricating oil cuts causes the oil cut to be unstable and decreasing product’s quality. As another example, the presence of sulfur compounds in many industries, in addition to imposing a high expenditure for applying suitable materials, disrupts the performance of many catalytic processes.
One of the conventional methods of eliminating the mentioned problems is the use of hydrogen in order to saturate hydrocarbon compounds to remove undesirable compounds such as sulfur oxides in the form of H2S. Despite the fact that the use of hydrogen in the sulfur removal unit is costly and the relevant process is usually carried out at high temperature and pressure (based on hydrocarbon cutting compounds), the application of hydrogen desulfurization method (Hydro treatment) is one of the common methods in desulfurization.
There are various methods of hydrogen production in industries, which are designed and selected according to the declared site condition as well as the required capacity or the presence of water resources. Among the common methods of hydrogen production, the following can be mentioned:
- Hydrogen production by Steam Reforming method
- Hydrogen production by Dry Reforming method
- Hydrogen production by Electrolyze method
Among the methods mentioned above, the third method is usually applicable for lower production ranges, and methods 1 and 2 are almost similar, with the difference that in the second method, methane reacts with CO2 and leads to hydrogen production. This method is less take into account compared to the Steam Reforming method. One of the major problems of this method is the possibility of cock formation.
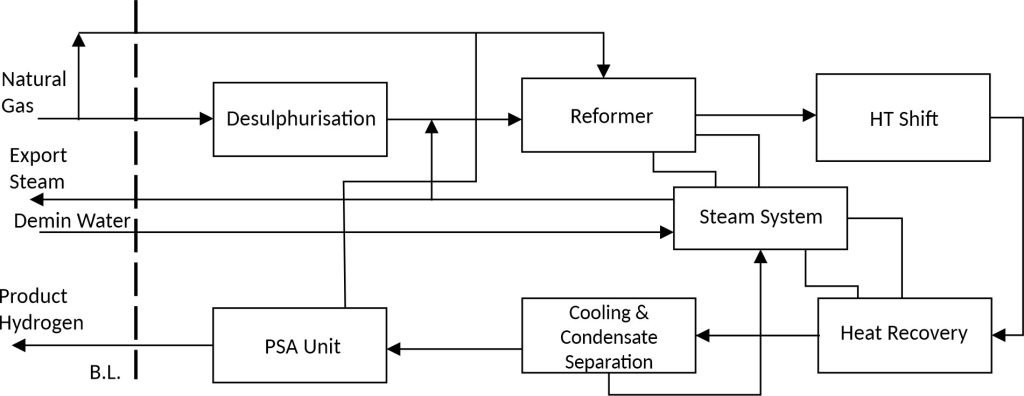
According to the mentioned methods, the main hydrogen production process in industries is Steam Reforming method or Wet method. In this process, methane (or natural gas) is usually received at a pressure of 20 to 25 barg and ambient temperature. In the next step, after preheating it enters sulfur removal reactors. These reactors convert mercaptan compounds into H2S by a part of the hydrogen produced in the hydrogen generation unit in the presence of a catalyst, and then these compounds are chemically absorbed in the next vessel. the logic behind this step can be stated that the presence of sulfur compounds leads to the poisoning of the reformer catalysts and will disrupt its performance. As the steam methane reforming is an endothermic reaction, it will take place in the radiation section of the furnace where the outlet temperature from this section is about 1000 C. Due to the very high temperature of this section, a heat recovery unit is regarded, in which the required steam is generated. It should be noted that the steam produced in this section will also be used as steam-methane reforming unit feed. Due to the fact that the reformer’s outlet stream contains some unreacted compounds, after cooling, these components go through the water-gas shift reactor to convert CO and unreacted water vapor into hydrogen and CO2 according to the reaction. This reaction is exothermic and one of the reasons why the temperature of the components decreases before entering the shift reactor is the exothermic nature of the reaction. Using the shift reaction is important from two aspects, one is the re-production of hydrogen and the other is the conversion of CO to CO2. Due to the larger molecular size of CO2, in the continuation of the process, if the PSA process is used, it leads to a better purification of the produced hydrogen. Figure 1 briefly illustrates the hydrogen production process diagram through Steam methane reforming method completes with PSA unit.
Because of the specific operational conditions of the Reformer unit in terms of temperature and applying Hitech catalysts, limited companies in the world are able to design, implement and launch such plants. Relying on its up-to-date engineering knowledge, HAVAYAR Industrial Group is capable of designing, constructing, pre commissioning and commissioning a steam methane Reforming unit with a capacity of 100 to 200,000 normal m3/hr at pressures up to 300 barg. Also, relying on the ability to provide all types of adsorbents , this company is capable of designing, constructing, pre commissioning and commissioning PSA units in order to achieve high purity of hydrogen up to 99.999%.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are various methods of hydrogen production in industries, which are designed and selected according to the declared site condition as well as the required capacity or the presence of water resources. Among the common methods of hydrogen production, the following can be mentioned:
-
- Hydrogen production by Steam Reforming method
- Hydrogen production by Dry Reforming method
- Hydrogen production by Electrolyze method
The main process of hydrogen production in industries is using Steam methane reforming method or so called Wet method.
sales department
after sales service
datasheet
catalogue
